Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Web Hosting?
- Types of Web Hosting
- How Web Hosting Works
- What is Domain Hosting?
- How Domain Hosting Works
- The Role of Domain Registrars
- Web Hosting vs. Domain Hosting: Which One Do You Need?
- How Web Hosting and Domain Hosting Work Together
- Choosing the Right Web and Domain Hosting Providers
- Factors to Consider for Web Hosting
- Factors to Consider for Domain Hosting
- Emerging Trends in Web and Domain Hosting
- Common Misconceptions About Hosting
- Conclusion
-
-
Introduction
When setting up a website, web hosting and domain hosting are two critical components. While they have different purposes, many individuals get confused or believe that web hosting and domain hosting are the same. In this blog, we’ll discuss the key differences between web hosting and domain hosting, the way web hosting and domain hosting work, and how to choose the best hosting option for your specific needs. Understanding these fundamentals is essential when selecting hosting providers. We will also explore some of the new trends in hosting that include cloud-based hosting and security features.

-
-
What is Web Hosting?
A web hosting service allows individuals and organizations to store website files and deliver them to website visitors. Web hosting companies maintain servers that store and deliver website files to visitors. Reliable web hosting services provide optimal website speed, security and uptime, which are crucial for businesses aiming to increase their online visibility.
-
-
The least expensive option is
shared hosting, where multiple websites are given access to the same server resources.
Dedicated hosting provides a website with its own server to maximize performance. Conversely,
virtual private server (VPS) hosting provides a larger degree of control and scalability.
Cloud hosting is ideal for websites that expect high traffic because it is reliable and very expandable. If you use managed hosting, you can rest assured that you will not have to worry about security, updates, or maintenance. In recent years, green hosting has grown in popularity, providing eco-friendly servers to reduce our carbon footprint.
-
-
A website’s files are hosted on a web server, which can be in the form of HTML and CSS files, images, and scripts. When a user types a website URL, their browser sends a request to the web hosting server, and the server retrieves the required files, which are then displayed in the user’s browser. In addition to this, web hosting is now facilitating faster loading times for the user, thanks to the emergence of edge computing and content delivery networks (CDNs). Edge computing and CDNs allow the data to be delivered to the user from the closest server, in addition to storing the file(s) on the host server.

-
-
What is Domain Hosting?
A domain hosting service is one that keeps track of domain names and ensures they resolve to the correct web servers. A domain name is essential for website accessibility and creating a brand image. Businesses can acquire a domain name that is memorable and search engine optimized through professional domain registration services. Blockchain domains are gaining traction in 2025, providing more security and decentralized services
-
-
A domain registrar functions by linking the domain name to the DNS (Domain Name System) when registering a domain name. As a result, when users type a domain name into their web browser, the DNS converts the human-readable domain name into an IP address, connecting the user to the appropriate web server. You want to choose a domain hosting provider that has good DNS management to ensure that your website, domain name, and IP address can work together seamlessly. Additionally, companies now have advanced AI-powered domain management and acquisition tools, which help companies select and refine domain names, particularly based on SEO trends.
-
-
- The Role of Domain Registrars
Domain registrars are authorized businesses that allow users to register and operate domain names. Some of the more popular domain registrars are GoDaddy, Namecheap, Google Domains, and Bluehost. When choosing a registrar, pay attention to pricing, security features, and renewal terms. There are now privacy-oriented domain registration options to keep a website owner’s information private so it does not show in a public WHOIS database.
-
-
Web Hosting vs. Domain Hosting: Which One Do You Need?
Both web hosting and domain hosting are vital components of a website, but they have different functions. If you’re creating a new website, you’ll likely have both web hosting and domain hosting. If you own a domain name but haven’t built your website yet, you may only need domain hosting until you’re ready to purchase web hosting. Some businesses may want to register multiple domains for branding before the website is launched. Understanding which service you need at each stage of your online presence will help maximize your costs and resources.
-
-
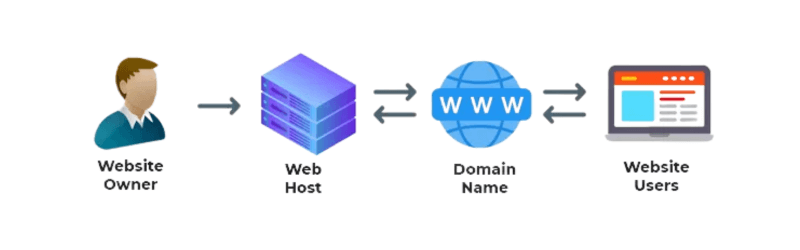
How Web Hosting and Domain Hosting Work Together
While web hosting and domain hosting are not the same service, they work collaboratively to bring a website online. Domain hosting provides a domain name, which has to be linked to the web hosting provider through proper DNS settings. When a user types the domain name into a web browser, the DNS will know where to direct the request on the internet, pulling the appropriate web server. The web server finds the requested website files and downloads them for display in the user’s browser. A high-ranking web hosting provider also should provide domain management, which is critical for the proper performance of the website and what search engines will report as search engine optimization (SEO). Finally, AI-based DNS management is now used to help speed websites while reducing downtime.
-
-
Choosing the Right Web and Domain Hosting Providers
- Factors to Consider for Web Hosting
Performance is important when selecting a web hosting provider. You need fast server speeds, high uptime guarantees, and security features including SSL certifications and DDoS protection. Scalability is also important, especially if you anticipate traffic increases to your website. Customer service should be responsive and available around-the-clock to assist with technical issues. Hosting providers such as
Scopehosts, Bluehost, SiteGround, and HostGator are some names you might recognize. Serverless hosting, which allows companies to run websites without managing conventional servers, is becoming very popular.
-
-
- Factors to Consider for Domain Hosting
Before obtaining a domain, it is advised to compare alternatives since there are different prices and renewal fees associated with different domain registrars. Research what types of control panels are available since DNS management can become cumbersome even at other domain registrars if the control panel is not user friendly. Furthermore, additional enhancements such as a WHOIS privacy protection service, domain forwarding, and email hosting are features offered by certain companies. Reliable domain hosting is an assurance of heightened website security and improved search engine results. Other alternatives to conventional domain hosting are emerging from Ethereum Name Service (ENS) and other decentralized name systems.

-
-
Emerging Trends in Web and Domain Hosting
- Edge Computing and CDN Integration – Hosting providers are incorporating edge computing to enhance website load speeds.
- AI and Machine Learning in Hosting – AI powered tools are improving server maintenance, security, and performance monitoring.
- Blockchain-Based Domains – Decentralized domain services are becoming more popular for privacy and security.
- Eco-Friendly Hosting – Green hosting providers are using renewable energy to power data centers.
- Quantum Computing Impact – Early-stage developments in quantum computing may redefine encryption and hosting security.
- Common Misconceptions About Hosting
A lot of people think that domain hosting and web hosting are the same service, which is not true. They also think that you have to buy both services from the same company. You can buy your domain from one company and host your website with another company. People think that when you buy a domain name, you own it, and that is true, but they do not understand that you must renew that domain name from time to time.
Conclusion
It’s important to comprehend how web hosting is different from domain hosting for any successful web page project. You’ll need web hosting for the infrastructure to build your site and domain hosting to let people discover your site via an easily remembered name. Furthermore, with trends such as blockchain domains, AI hosting, and edge-hosted computing, the range of industry options has never been more advanced. Selecting the right hosting provider for your purpose assures your website in a digital ecosystem is secure, scalable and performs well.